Assam Government Takes Step to Protect Poba Reserve Forest by Designating it as a Wildlife Sanctuary
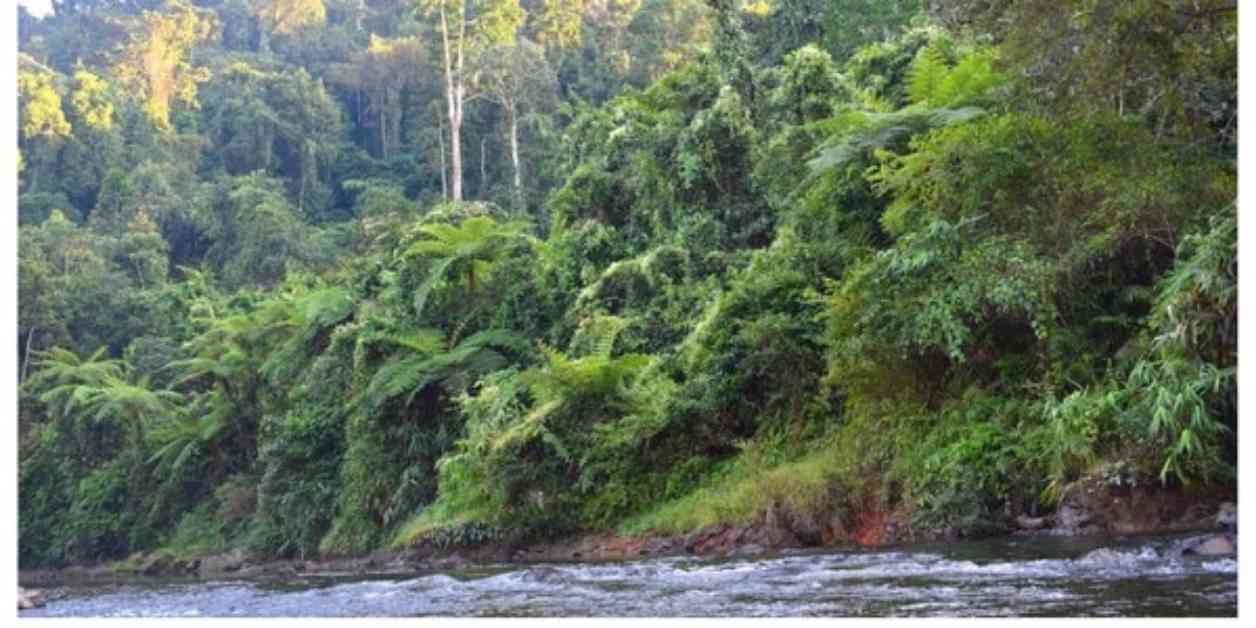
The Assam Government has taken a significant step towards conservation by announcing the designation of the Poba Reserve Forest as a wildlife sanctuary. This rainforest, located in the northeastern part of Assam, is home to a diverse range of flora and fauna, making it an essential ecosystem to protect.
Expansion of Protected Area
The proposed Poba Wildlife Sanctuary will cover an area of 257.29 sq km, including not only the Poba Reserve Forest but also the Kabu Chapri Proposed Reserve Forest and the surrounding riverine areas. By expanding the protected area, the government aims to safeguard the natural resources and biodiversity of the region for future generations.
Commitment to Conservation
State Environment and Forest Minister Chandra Mohan Patowary emphasized that the decision to designate the Poba Reserve Forest as a wildlife sanctuary demonstrates the government’s commitment to conservation and sustainable development. By preserving this rich ecosystem, the government is ensuring the protection of wildlife habitats and promoting biodiversity conservation in the state.
Significance of Poba Reserve Forest
The Poba Reserve Forest is known for its abundant wildlife, serving as a crucial migratory route for various animals, especially elephants. This forest corridor connects the D’ Ering Memorial Wildlife Sanctuary, Kabu Chapri Proposed Reserve Forest, and Dibru-Saikhowa National Park, providing a vital passage for wildlife movement in the region.
According to an official statement, the Poba Reserve Forest is the second significant elephant migration route from the north to the south bank of the Brahmaputra river, with herds of approximately 70-80 elephants crossing the river at different times. Male elephants utilize these routes throughout the year, highlighting the importance of preserving this corridor for their movement.
Diverse Wildlife and Ecosystem
The Poba Reserve Forest is home to a wide variety of arboreal species, including the slow loris and capped langur. Additionally, the forest houses common mammal species such as the wild boar, contributing to the rich biodiversity of the region.
Apart from mammals, the forest also supports a diverse range of bird and reptile species, with approximately 45 different species inhabiting the area. The confluence of the Siang and Lohit rivers within the forest creates a unique habitat for various fish species, further enhancing the ecosystem’s biodiversity.
Moreover, the Poba Reserve Forest is renowned for its abundance of orchids, attracting nature enthusiasts and researchers alike. The forest’s rich flora and fauna make it a valuable asset for conservation efforts and a significant ecological hotspot in the region.
Preserving Natural Heritage
By designating the Poba Reserve Forest as a wildlife sanctuary, the Assam Government is not only protecting the region’s natural heritage but also ensuring the long-term sustainability of its ecosystems. This move reflects a proactive approach towards conservation and highlights the importance of safeguarding critical habitats for wildlife protection and biodiversity conservation.
In conclusion, the decision to designate the Poba Reserve Forest as a wildlife sanctuary is a commendable step towards preserving the rich biodiversity of the region. By expanding the protected area and promoting conservation efforts, the Assam Government is setting a positive example for sustainable development and environmental stewardship.