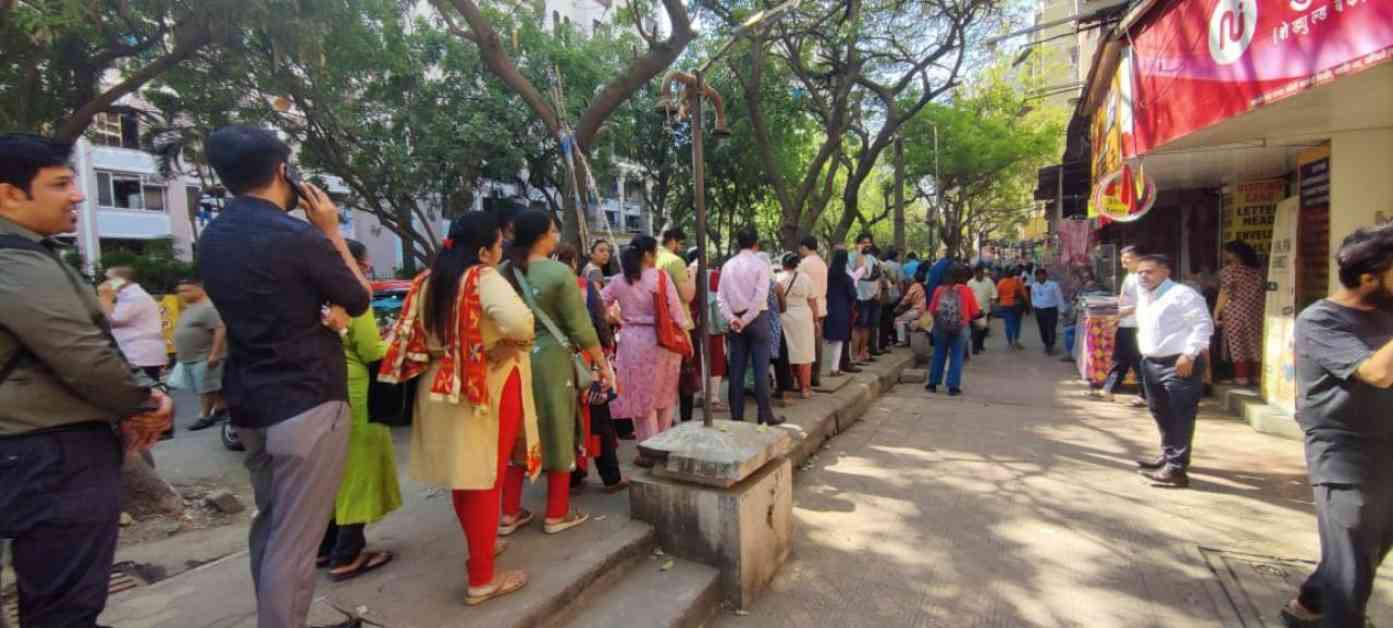
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has recently imposed strict restrictions on New India Co-operative Bank Limited, located in Mumbai, due to serious financial concerns. The central bank has prohibited the bank from granting loans, making investments, or allowing withdrawals without prior approval, effective from the close of business on 13 February 2025. This move has raised questions and concerns among depositors and the banking community alike.
Why has the RBI taken such drastic action against New India Co-operative Bank? The official notice from the RBI cites “supervisory concerns arising from recent material developments” at the bank as the primary reason for the restrictions. While the exact nature of these concerns has not been disclosed, it is evident that the bank’s financial stability is in jeopardy, potentially jeopardizing the funds of depositors.
The financial struggles of New India Co-operative Bank have been apparent in recent years, with consecutive losses reported in the financial years ending March 2024 and March 2023. The bank’s advances have also declined significantly, indicating a shrinking loan portfolio. These financial indicators have likely contributed to the RBI’s decision to step in and impose restrictions to protect the interests of depositors and ensure the stability of the banking sector.
What specific restrictions has the RBI imposed on New India Co-operative Bank? The central bank has prohibited the bank from granting or renewing loans and advances, making fresh investments, borrowing funds or accepting new deposits, and disbursing payments except for essential expenses like salaries and utility bills. Additionally, the bank is not allowed to sell, transfer, or dispose of its assets without prior approval from the RBI. Depositors, however, can rest assured that they will be able to claim up to Rs 5,00,000 under the Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation (DICGC) scheme.
Despite these stringent restrictions, the RBI has clarified that the bank’s license has not been cancelled, and it will continue to operate under close supervision. The restrictions will remain in force for six months, during which the RBI will closely monitor the bank’s financial condition and take necessary actions to address any underlying issues.
The situation at New India Co-operative Bank is reminiscent of past interventions by the RBI, such as the action taken against Punjab and Maharashtra Co-operative Bank in 2019 due to financial irregularities. In that case, a new entity eventually took over the struggling bank, highlighting the potential outcomes of such interventions.
As the banking community and depositors await further developments, the RBI has assured that it will continue to monitor the situation and take additional actions as needed to safeguard the interests of depositors. This serves as a reminder of the importance of financial stability and regulatory oversight in the banking sector to ensure the safety and security of customers’ funds.
In conclusion, the RBI’s restrictions on New India Co-operative Bank underscore the critical role of regulatory authorities in maintaining financial stability and protecting the interests of depositors. As the situation unfolds, stakeholders will be closely watching for updates and developments to ensure the long-term viability and sustainability of the banking sector.